Some tips on tools and environment configuration or related knowledge concepts are recorded here.
Modifying Linux File Permissions
Each file in Linux has 9 permission bits, which can be divided into three categories:
| - | Read (read) | Write (write) | Execute (execute) | - |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Owner (user) | r | w | x | 7 |
| Group (group) | r | w | x | 7 |
| Other (other) | r | w | x | 7 |
| - | 4 | 2 | 1 | - |
Use chmod in Linux to modify file permissions.
If you need to add executable permission for user to a file, simply put, there are two methods:
Assuming there is a file named test, and the current permission is -wxr-xwr-(356), we want to add read permission for user, write permission for group, and execute permission for others.
The first method: use u to represent users, g to represent groups, and o to represent others.
1 | chmod u+x test |
The second method is to use numeric setting, as seen from the table above, r is 4, w is 2, and x is 1. Add the values you want to set for the three bits (user/group/other):
The previous method modifies permissions somewhat tedious; here we can directly specify the permissions of u/g/o:
1 | chmod 777 test |
Virtual Machine Network Configuration
Set one of the virtual network cards (VMnet0) to bridge to the physical network card under VMware - Edit - Virtual Network Editor.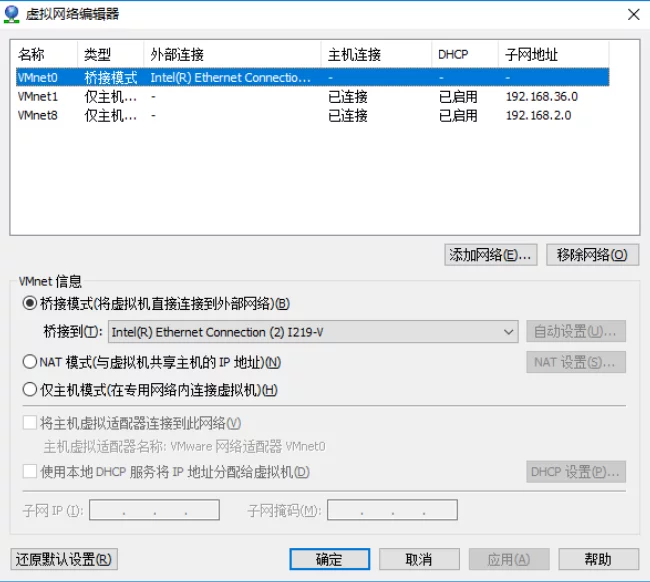
Then modify the Network Adapter in the Virtual Machine Settings to the virtual network card (VMnet0) we just edited.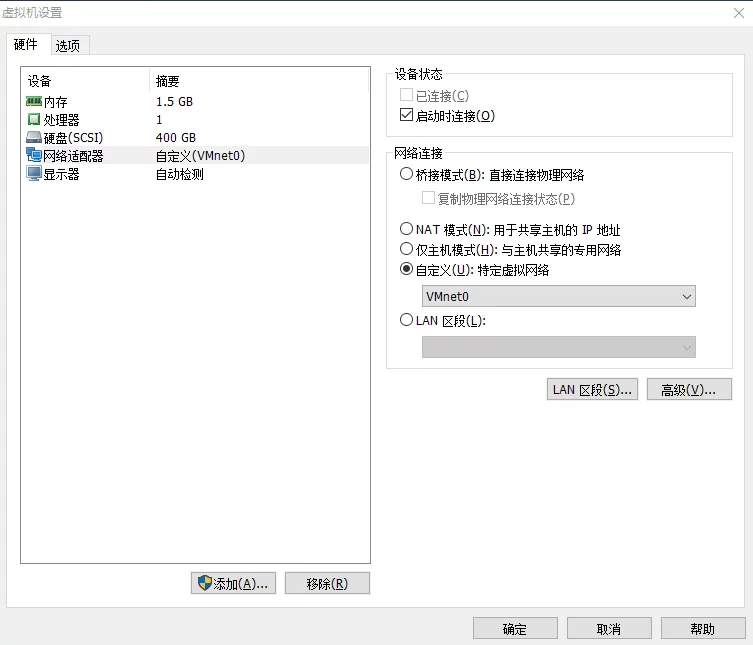
Next, restart the system and use ifconfig to check if it’s on the same subnet as the LAN.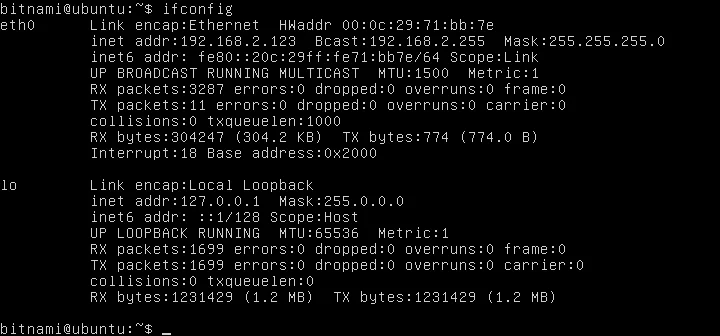
Since the IP is dynamically assigned by the router, it may change after a reboot. You need to set a static IP.
Edit /etc/network/interfaces, changing from
1 | auto eth0 |
to (modify the gateway and IP address to your local network configuration):
1 | auto eth0 |
Finally restart.
You can also add a custom DNS server:
1 | #DNS configuration |
Meaning of Numbers Output in man Command
We use man to check an interface, for example, fork: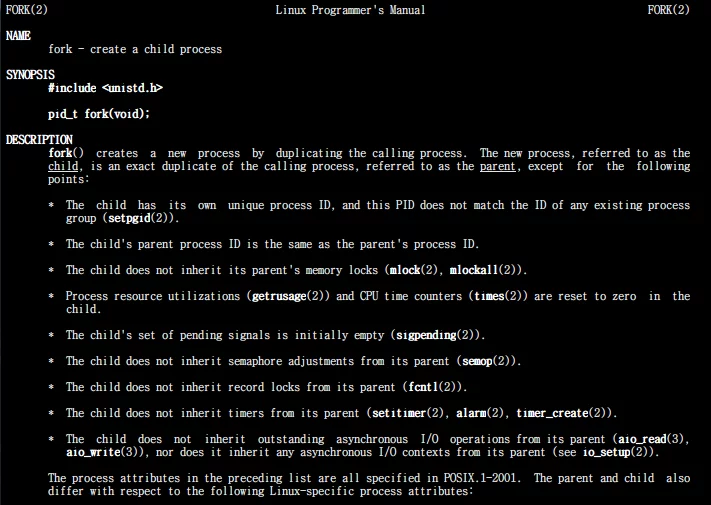
Note the fork(2) at the top left and top right, what does this number 2 represent? (different parameters have different meanings in man)
You can check with man man:
You can see that 1~9 represent different interface categories:
1: Executable programs or shell commands
2: System calls (functions provided by the kernel)
3: Library calls (functions within program libraries)
4: Special files (usually found in /dev)
5: File formats and conventions e.g. /etc/passwd
6: Games
7: Miscellaneous (including macro packages and conventions), e.g. man(7), groff(7)
8: System administration commands (usually only for root)
9: Kernel routines [Non standard]
Differences Between SJLJ/DWARF/SEH in MinGW Version
SJLJ (setjmp/longjmp)
available for 32 bit and 64 bit
not “zero-cost”: even if an exception isn’t thrown, it incurs a minor performance penalty (~15% in exception-heavy code).
allows exceptions to traverse through e.g. windows callbacks
DWARF (DW2, dwarf-2)
available for 32 bit only
no permanent runtime overhead
needs the whole call stack to be dwarf-enabled, which means exceptions cannot be thrown over e.g. Windows system DLLs.
SEH (zero overhead exception)
For more details see MinGW-64-bit - QtWiki
System Paths in Windows
| System Path Meaning | System Path (case insensitive) | Corresponding Absolute Path |
|---|---|---|
| Current System Drive | %systemdrive% or %HOMEDRIVE% | C:\ |
| Current System Directory | %SystemRoot% or %Windir% | C:\WINDOWS |
| Current User Folder | %UserProfile% or %HOMEPATH% | C:\User\UserName |
| Public Application Data Folder | %AllUsersProfile% | C:\ProgramData |
| Temporary Folder | %TEMP% | C:\Users\UserName\AppData\Local\Temp |
Markdown
Preventing Markdown from Truncating Parentheses in Links
To create a link or image with Markdown, use [title](link) and ; however, when the Markdown link contains parentheses, the markdown syntax will match the parentheses in the link, causing the link to be split into two parts.
1 | # This causes the link to be matched as https://imzlp.com/ar(chi |
The solution is to use %28 instead of ( and %29 instead of ). This is primarily because ) will ambiguously signify the end of the link.
1 | # OK. https://imzlp.com/ar(chi)ves/ |
This uses URL encoding to replace ASCII characters to solve the issue.
Using Quotation Marks in Titles and Directories
Using " directly in titles in Markdown may be escaped, so you can use " instead. For more character escape options, see: HTML Escape Character Reference.
Mathjax Not Parsing Some Instances
Note when using subscript _ in Mathjax within markdown, make sure to write it as \_, or it may lead to parsing issues.
Visual Studio
Disabling VS’s Built-in Spell Check
Tools - Options - Text Editor - C/C++ - Advanced:
Change Disable Squiggles to true.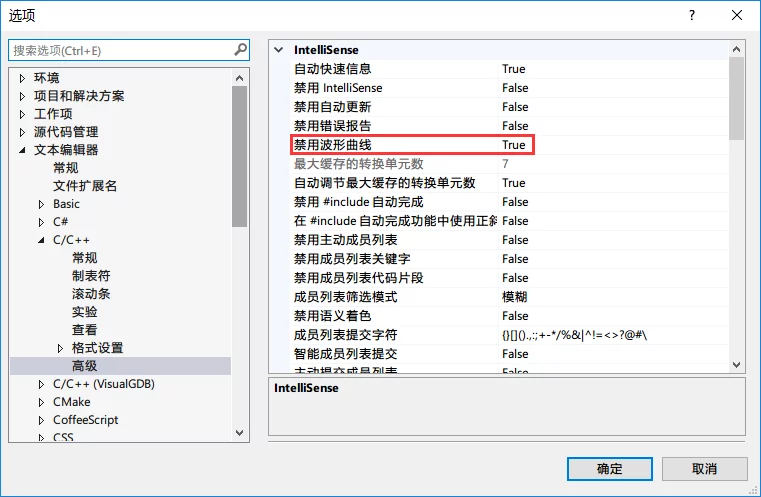
Disabling Spell Check in Visual Assist
When using Visual Assist in VS and entering Chinese comments, there will be red wavy lines which can be distracting.
In VAssistX - Visual Assist Options, find Underlining on the left side and uncheck Underline spelling error in comments and strings using: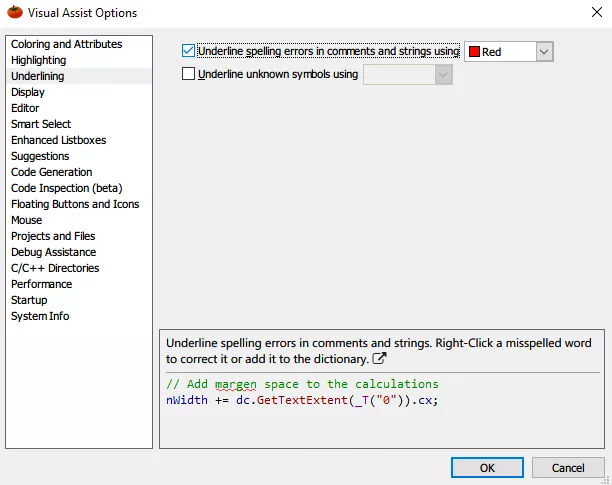
Uncheck it.
Mismatches Between Source File and Module Generation
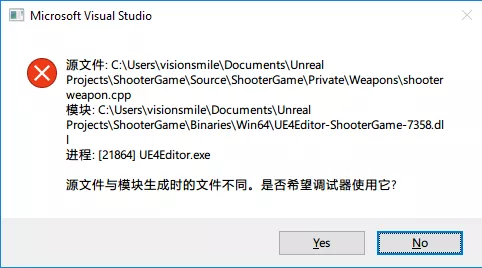
You may encounter this situation when debugging attached to a process. The solution is:
Open VS: Tools - Options - Debugging - General, and uncheck “Enable Address-Level Debugging” and “Require source files to exactly match the original version”.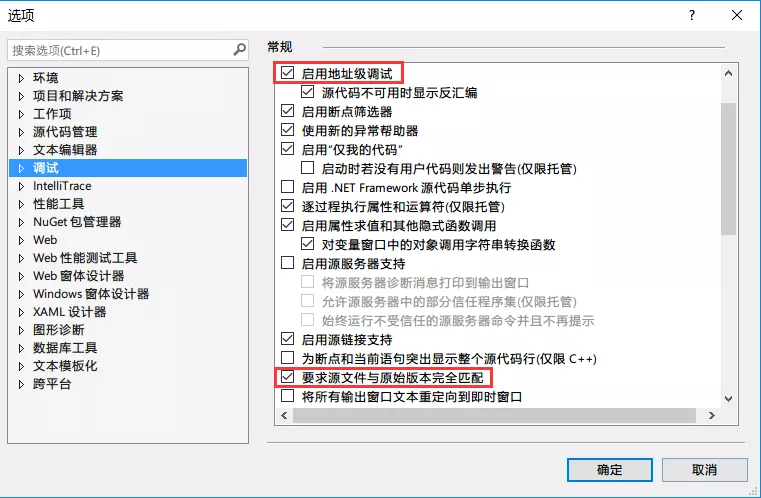
Then reattach to the process for debugging.
Enabling Latest Draft Standards for Modules
For specific links, see: Using C++ Modules in Visual Studio 2017
First, add Standard Library Modules during VS installation, then set the following three options in project properties:
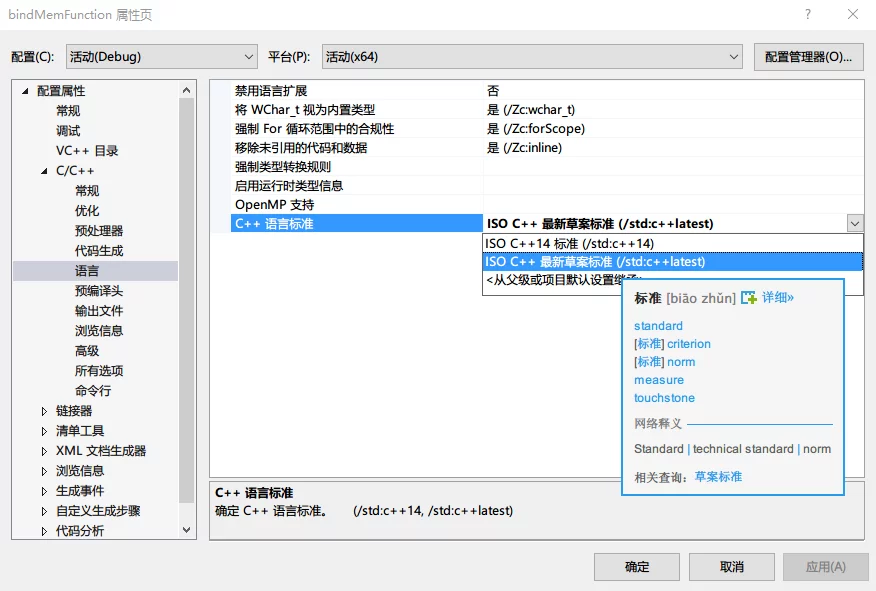
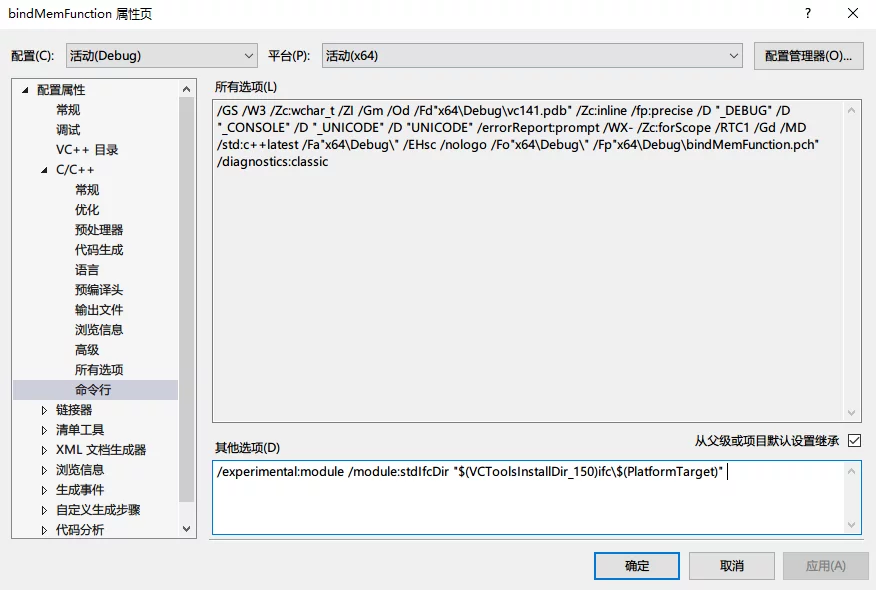
The command to fill in the command line in the image above is:
1 | /experimental:module /module:stdIfcDir "$(VCToolsInstallDir_150)ifc\$(PlatformTarget)" |
Windows Tips
Removing Quick Access from Windows 10 File Explorer
After opening This PC, there are things like Downloads / Videos / Documents, which seem unnecessary. You can delete them using the method below.
Save the following code as .reg and execute it.
1 | Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 |
Bat Tips
Getting the Current Directory Name in bat
1 | @echo off |
Getting the Current Directory in bat
1 | echo Current drive and path:"%~dp0" |
Checking if a File Exists in bat
1 | @echo off |

