Recently, I have been using Protobuf in VS, and I will briefly record the process of building Protobuf using MSVC.
The method for compiling protobuf on Windows introduced in this article has several software requirements:
- Git
- cmake
- visual studio
First, pull the protobuf source code:
1 | $ git clone -b 3.5.x git@github.com:google/protobuf.git protobuf-3.5.x |
Then pull googletest:
1 | $ git clone git@github.com:google/googletest.git |
Then, change the directory to protobuf-3.5.x/cmake:
1 | $ cd protobuf-3.5.x/cmake |
Execute the following command, changing "Visual Studio 14 2015" to the version of Visual Studio you are using; you can check this by using the command cmake -G. Note that you need to specify the architecture [arch] information; if you do not specify Win64, it defaults to Win32. The DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX specifies the directory for installing protobuf (copying the compiled files).
1 | cmake -G "Visual Studio 14 2015 Win64" -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX="~/protobuf" |
If there are no errors, execute the following:
At this point, it will generate protobuf.sln and extract_includes.bat and other files under the cmake directory.
First, executing extract_includes.bat will copy the .h and .cpp files needed by protobuf (in the include/google folder) to the cmake directory.
Then use VS to open protobuf.sln, change the red box to Release, right-click ALL_BUILD to compile (generally you only need protobuf and protoc).
Note: If you are using Protobuf in Unreal, the runtime library options need to be changed to
/MD(Release) and/MDd(Debug).
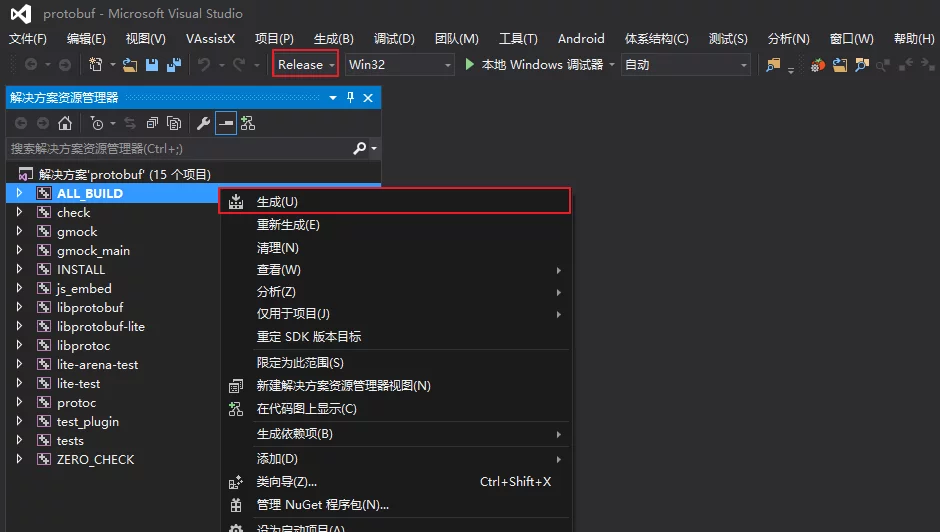
After a successful execution, there will be a generated Release directory in the cmake directory.
At this point, the compilation work is done.
However, the compiled files are all in the cmake directory, and for convenience, we need to install the compiled files (moving the compiled files to the directory specified earlier with -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX="~/protobuf").
You just need to execute the build on the INSTALL project in VS:
Then the directory structure of ~/protobuf should be as follows:
1 | protobuf/ |
Then add Protobuf/bin, Protobuf/lib, and Protobuf/include to the system PATH.
Attached is my compiled protobuf_v3.5.1, where the lib/MD and lib/MT are different multithreading runtime libraries, with debug being /MTd and /MDd and release being /MD and /MT.
Then you can write a simple test case:
1 | // zlp.PeopleInfo.proto |
Use protoc to generate .h and .cpp:
1 | $ protoc zlp.PeopleInfo.proto --cpp_out=./ |
This will generate zlp.PeopleInfo.pb.cc and zlp.PeopleInfo.pb.h in the current directory of zlp.PeopleInfo.proto.
- Then create a new console project in VS and add the two generated files to the project.
- In the project settings, add the protobuf header file include directory, Properties > C/C++ > General > Additional Include Directories.
![protobuf-add-include-folder]()
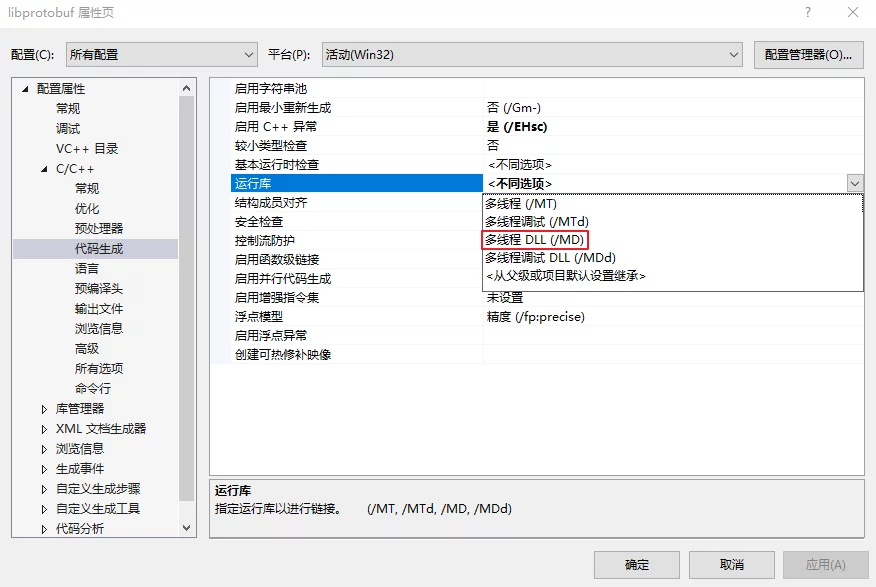
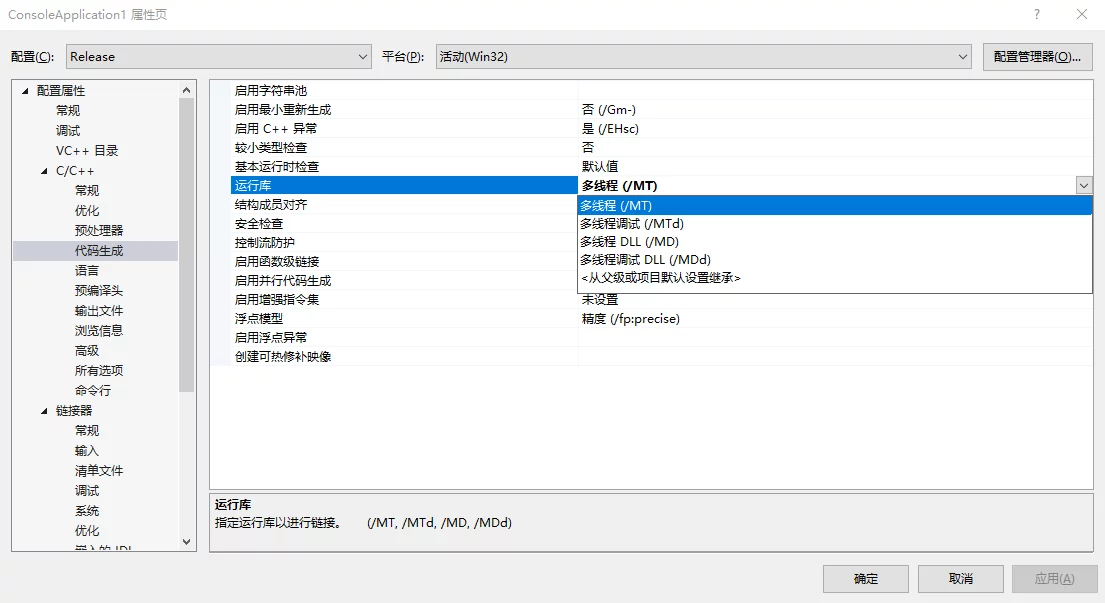
- Modify the project settings under Properties > C/C++ > Code Generation > Runtime Library to be
/MTor/MD(Release) or/MDor/MDd(Debug).![protobuf-setting-libraray-thread-mode]()
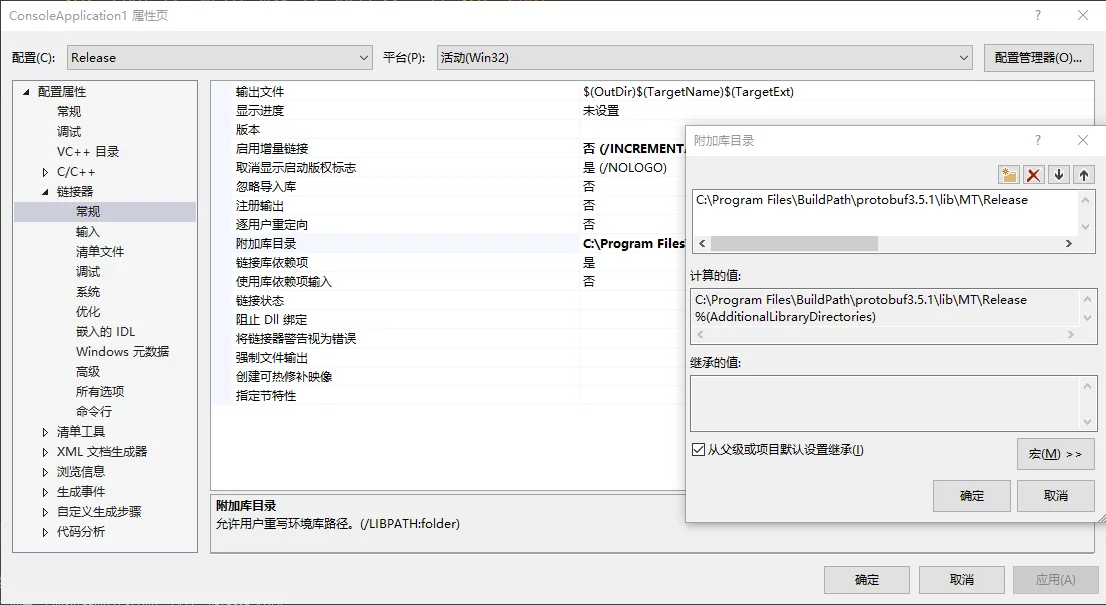
- In the project settings, add the protobuf link library directory, Properties > Linker > General > Additional Library Directories, noting to specify the same runtime library mode as selected (
/MD//MT), or it will report an error.![protobuf-add-link-library-folder]()
- In the project settings, add the protobuf link files, we need
libprotobuf.libandlibprotoc.lib, under Properties > Linker > Input > Additional Dependencies.![protobuf-add-link-library-file]()
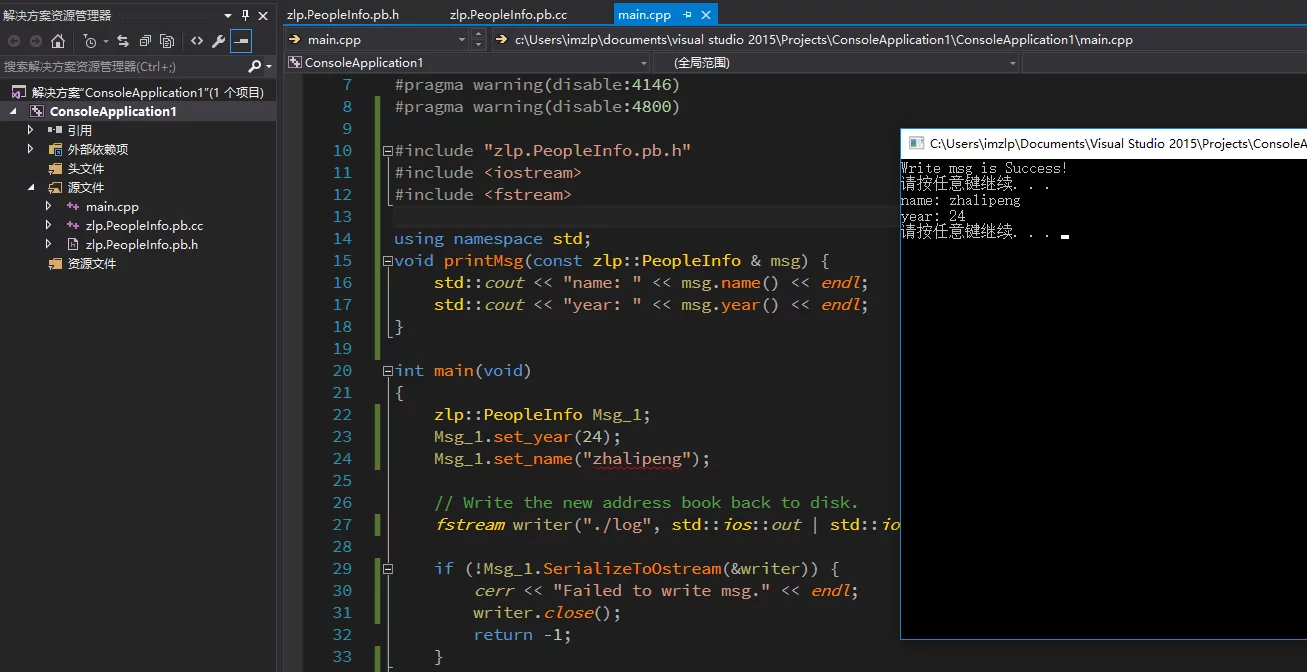
Once the settings are complete, here is a simple test code that serializes from protobuf to a file and then deserializes from the file:
1 |
|
Note: The code generated by protobuf may have some syntax or performance warnings, and you can disable certain VS warnings according to your needs. The warnings I disabled are as follows (placed at the top of the included header files):
1 |
The result of successfully compiling and running is as follows: